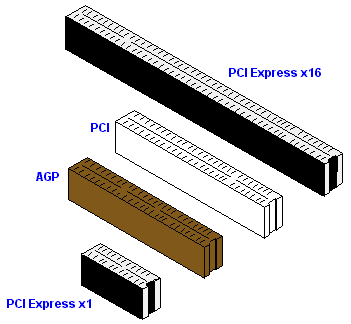
Bus Slot Type
- PC Card Slot Types. ISA; AGP; PCI; PCI-X; PCI-E (PCIexpress) ISA. ISA, or Industry Standard Architecture, is an 8bit or 16bit parallel bus system that allowed up to 6 devices to be connected to a PC. Virtually all IBM-compatible PCs made before the Pentium were based on the ISA (IBM's PC AT) bus.
- Classification of Power System Buses A bus in a power system is defined as the vertical line at which the several components of the power system.
- Given a PCI domain, bus, and slot/function number, the desired PCI device is located in the list of PCI devices. If the device is found, its reference count is increased and this function returns a pointer to its data structure. The caller must decrement the reference count by calling pcidevput.
The PCI bus is the most popular expansion bus use in today's computers PCI Card. PCI 64 and 32bit Slot AGP Introduced by Intel in 1997, AGP or Advanced Graphic Port is a 32-bit bus or 64-bit bus designed for the high demands of 3-D graphics. AGP has a direct line to the computers memory which allows 3-D elements to be stored in the system.


PCMCIA is an acronym for Personal Computer Memory Card InternationalAssociation; the acronym is pronounced as separate letters. PCMCIA isa non-profit trade association and standards body consisting of some500 companies. PCMCIA has developed a standard for small, creditcard-sized devices, called PC cards, that are often used in notebookcomputers. (Adapters are available that allow PC cards to be used indesktop computer systems.) You can visit the PCMCIA web site at:
In the past, the cards were known as PCMCIA cards, but they are nowreferred to as PC cards, PC card hosts, and PC card software.PCMCIA refers to the association and standards body.
A PC card slot is an expansion slot often found in notebook computersthat allows for the easy and quick addition of a host of differentdevices. Originally designed for adding memory to portablecomputer systems, the PC card standard has been updated several timessince its original creation.
PC cards are Plug and Play devices that are often hot-swappable (i.e.,cards may be removed and inserted with the computer power turned on,without rebooting) under Mac OS and Windows 95and beyond. (Windows NT, however, has more limited supportfor PC cards, and you cannot change cards on the fly.) Many systemswill give a familiar beep sound from the computer's speaker when youremove or insert a card.
Differences between PC cards
There are three different types of PC cards. All three have the samerectangular size (85.6 by 54 millimeters), but different thicknesses.
- Type I cards can be up to 3.3mm thick, and are used primarily for addingadditional ROM or RAM to a computer.
- Type II cards (the most common) can be up to 5.5mm thick. Thesecards are often used for modem, fax, SCSI, andLAN cards.
- Type III cards can be up to 10.5mm thick, sufficiently large forportable disk drives.
Differences between PC card slots
As with the physical PC cards, PC slots also come in three sizes:
Bus Slot Types
- A type I slot can hold one type I card
- A type II slot can hold one type II card, or two type I cards
- A type III slot can hold one type III card, or a type I and typeII card.
Most notebook computer systems come with two PC card slots that allowfor the use of two type I or type II PC cards and one type III PCcard. The PC card slots are stacked with one above theother. Usually, type III PC cards fit only in the bottom slot.
Common PC card devices
Following is a list of common PC card devices:
- CD-ROM interface
- Cellular phone interface
- Security tokens
- Docking station interface
- 10Mbps Ethernet LAN adapters
- 100Mbps Ethernet adapters
- GPS (Global Positioning System) cards
- Hard drives
- Infrared wireless LAN adapters
- ISDN cards
- Joystick interface cards
- Memory cards
- Modem and Ethernet combination cards
- Parallel port interface
- SCSI adapters
- Serial port interface
- Sound cards, input and output
- Video capture/frame grabber cards
- Video teleconferencing cards
Cardbus
Pci Bus Slot Types
Many laptop manufacturers now advertise their PC card slots as cardbuscompatible, or they simply identify the slots as cardbusslots. Cardbus is an extension of the latest PCMCIA standard, whichexpands the bus bandwidth and throughput to 32bits at 33MHz. In contrast, the older PC card standard was16 bits at 8MHz. Cardbus is analogous to the PCI slots in desktops,while the older PC card standard is analogous to ISA. The newercardbus slot can accommodate an older 16-bit PC card, but an older PCcard slot cannot accept newer cardbus cards. To tell if your PC cardis cardbus, look on the interface end of the card. Cardbus deviceswill have a notched metal plate on that end.
While not technically accurate, some vendors and technicians refer tothe older style 16-bit PC card as PCMCIA in order to contrast it with32-bit cardbus cards, which makes them sound like competingstandards. However, cardbus is an extension to the PCMCIA standard,not a replacement.
For additional information, see:
ExpressCard
Bus Slot Type
The latest extension of the PCMCIA standard is calledExpressCard. This standard is being built on the latest USB2.0 and PCI Express buses. The aim is to increase speed and reducesize, cost, and complexity. One of the ways it does this is toeliminate the PCMCIA Host Controller in favor of using the USB or PCIExpress controller directly.
For additional information, see: